Documentation
Skap Processing Guideline
Face Model - Base Mesh, and Topology
While the topology does not need to be perfectly uniform, it should be clean, readable, and reasonably optimized to ensure a smooth workflow and reliable results. Proper edge flow around key facial areas (eyes, mouth, nose) will help preserve facial features and surface continuity.
Avoid the following:
- Overly simplified topology (e.g. aggressive ZRemesher results with insufficient detail)
- Extremely dense meshes that are heavy and offer no real benefit
A balanced topology neither too light nor excessively dense provides the best foundation for SKAP processing and refinement.
We advise to set real-world scale (1:1) for the OBJ, while it is not requiered for Skap, it ensure accurate displacement and clean workflow down the line.
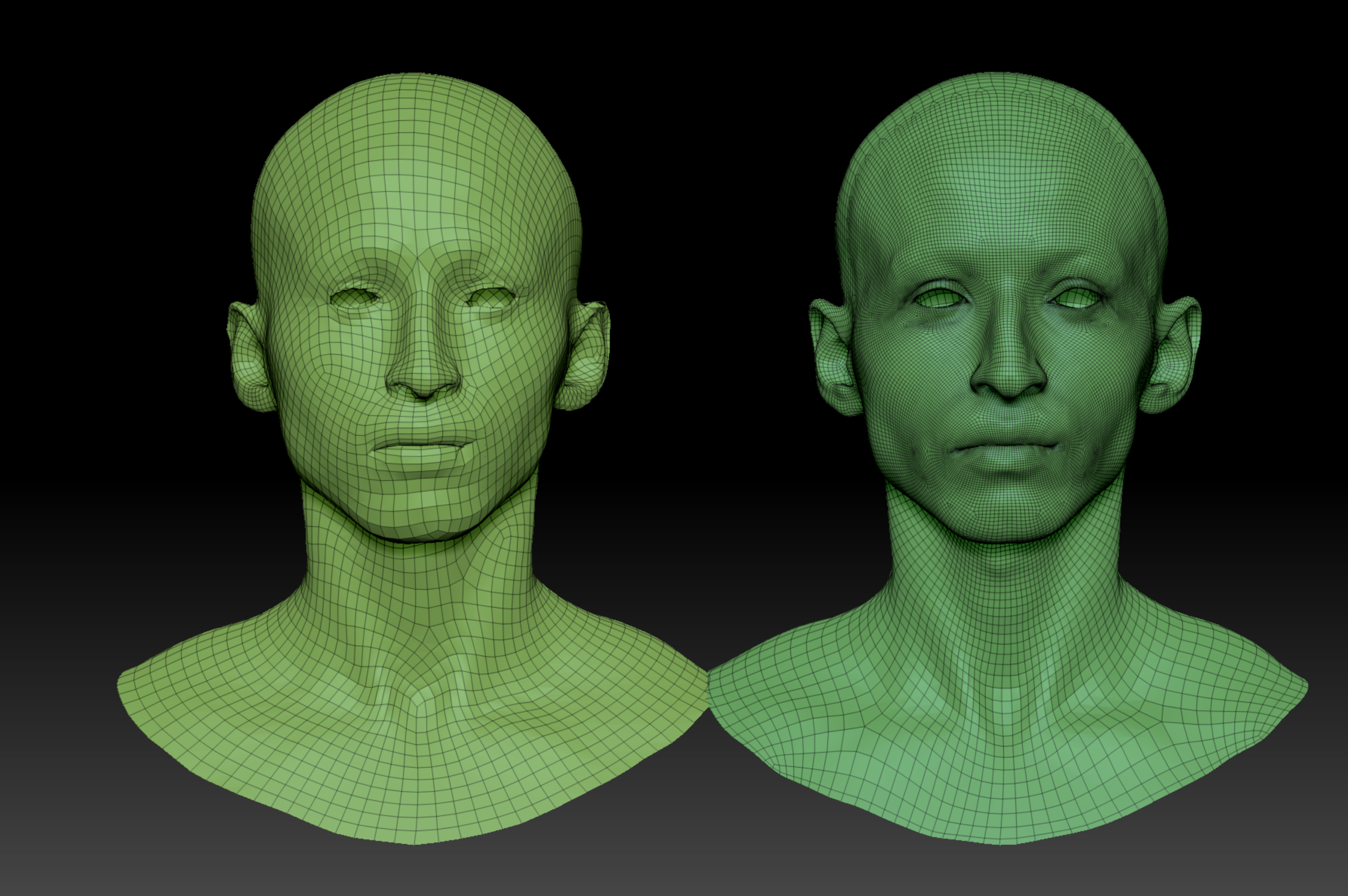

UVs - Layout and Requirements
The OBJ file is the essential requirement for SKAP, as it contains the geometry and UV layout needed for surface processing.
UV requirements:
- UVs must be clean, consistent, and optimized.
- The face should ideally occupy a large portion of the UV space (around two-thirds) to improve texture resolution and overall results.
- Avoid fragmented or disorganized layouts where facial features are cut apart or scattered.
- Ensure that critical facial areas are not placed on UV borders or split down the middle.
A poorly used UV space can significantly reduce the quality of SKAP results. For example, UV layouts that fail to use the full tile or leave large unused areas will waste valuable resolution and negatively impact fine detail reproduction.
When laid out correctly, a single UV tile offers ample resolution and clarity for facial assets.
MetaHuman, VFace, and 3DScanStore UV layouts are fully compatible with this system and already meet these requirements.
Resolution and Workflow choice
- Minimum accepted resolution: 2048 × 2048
- Recommended resolution: 8192 × 8192
SKAP can process either a
Displacement map
or a
Diffuse map
as input.
In all cases, always provide the version that contains the highest level of sharpness and detail.
Displacement workflow
If your displacement map contains the most detailed informations, it should be used as the primary input. (pores, wrinkles, skin features)
The displacement map must be clean and free of artifacts. It should include:
- A balance of macro details (primary forms and features)
- Micro details such as pores and fine wrinkles
- A natural skin flow and directionality across the surface
For manually sculpted assets, ensure the displacement carries enough meaningful detail for SKAP to interpret and enhance.
The richer and cleaner the displacement map, the better SKAP can analyze and reconstruct the skin surface.
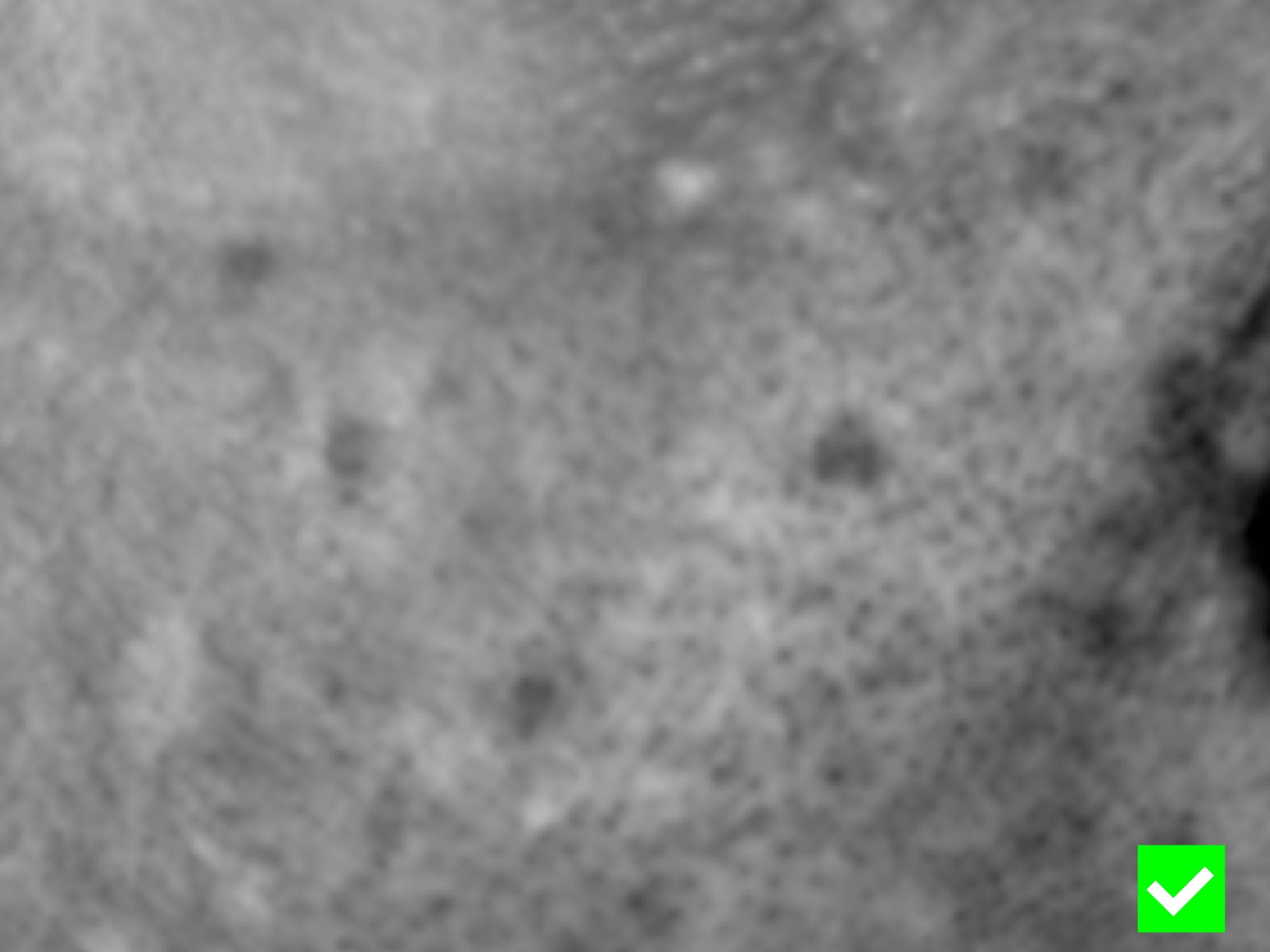


The displace workflow has two map types :
- Grayscale : The RED channel will be used.
- Multichannel The BLUE channel will be used.
To achieve the best results when using multichannel maps, it is mandatory to place the most detailed layer in the Blue (B) channel.
Diffuse workflow
If your diffuse map contains more usable surface detail than your displacement map, it can be used instead.
SKAP supports diffuse maps from photogrammetry or photometric scans, including assets where specular information is embedded in the color map. However, having clear and meaningful specular data is mandatory. The specular detail must visibly define the skin flow and surface direction. SKAP depends on these highlights to properly read and interpret the surface. Without well-defined specular information, the results will not be reliable.
When using a diffuse map, select the channel (R, G, or B) that shows the most visible surface detail.
This selected channel will serve as the base input for SKAP, effectively replacing a missing displacement map and allowing SKAP to generate a new, coherent displacement from it.
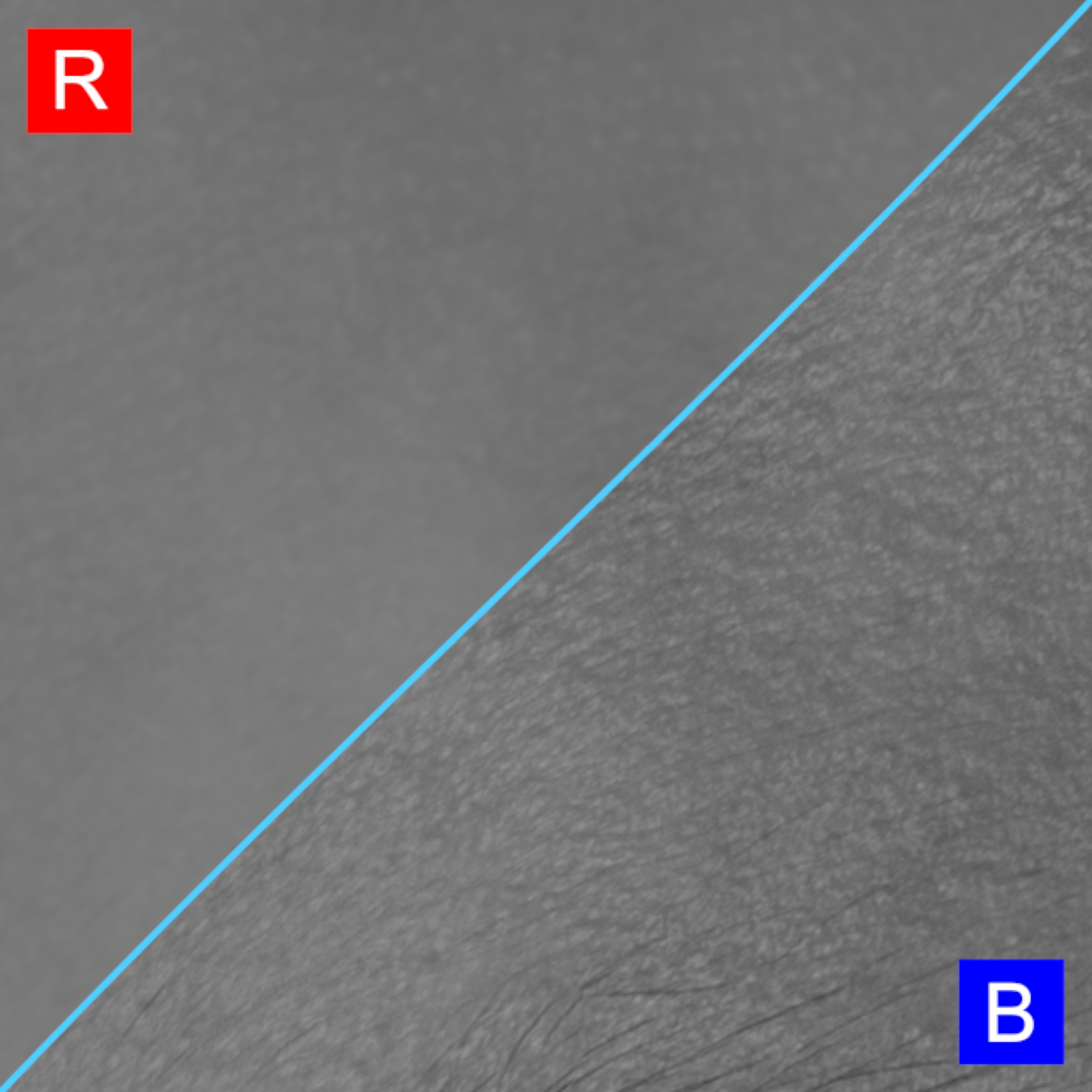
In this exemple the B channel is the most detailed and should be selected.
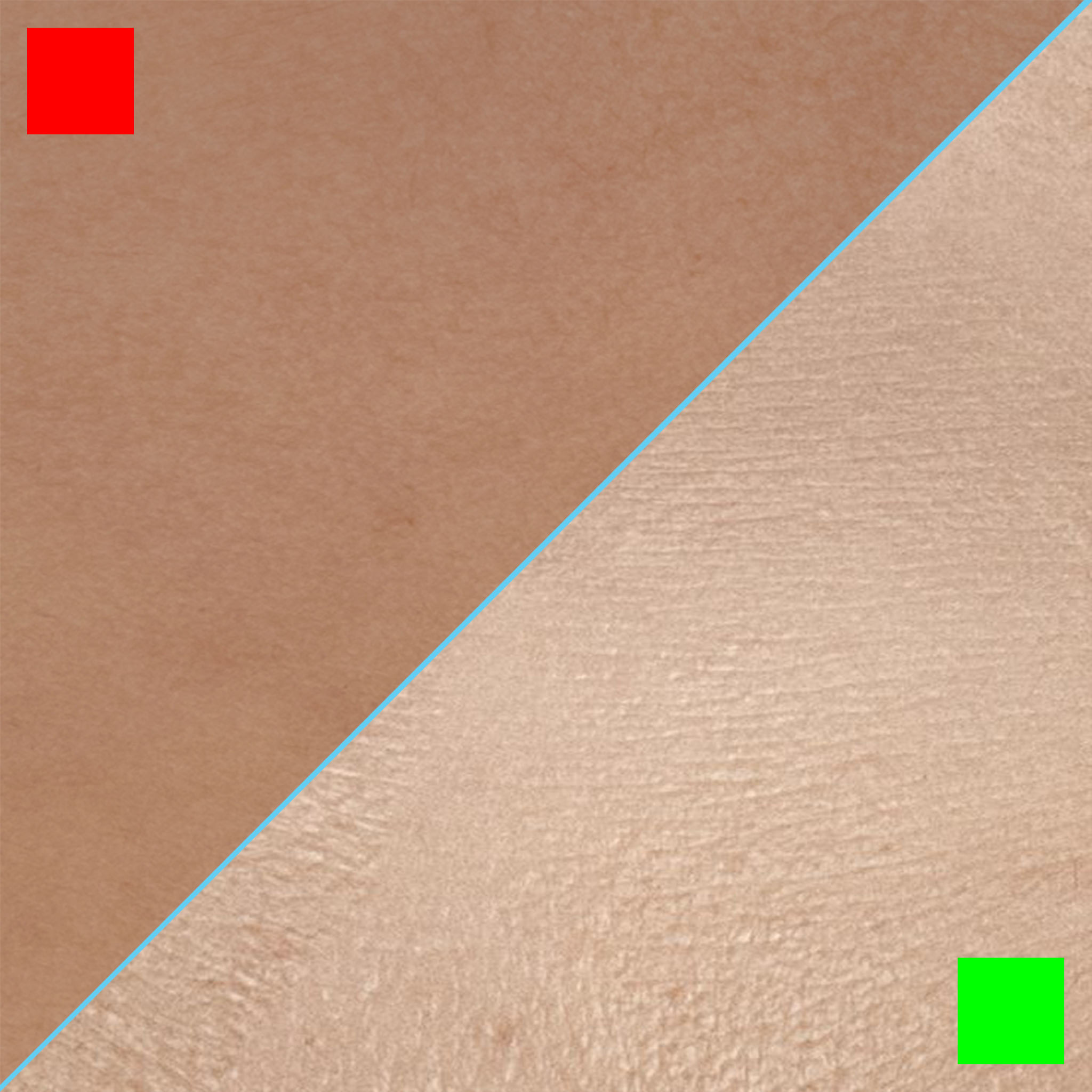

The input should have enough specular information to see a defined skin flow and surface direction.
Do not use an albedo map or cross-polarized texture without any specular information.
It is important to distinguish between:
- Diffuse maps, which should include lighting and specular information
- Albedo maps, which contain only pure skin color information
Albedo maps alone generally lacks sufficient surface detail and are not recommended as input.
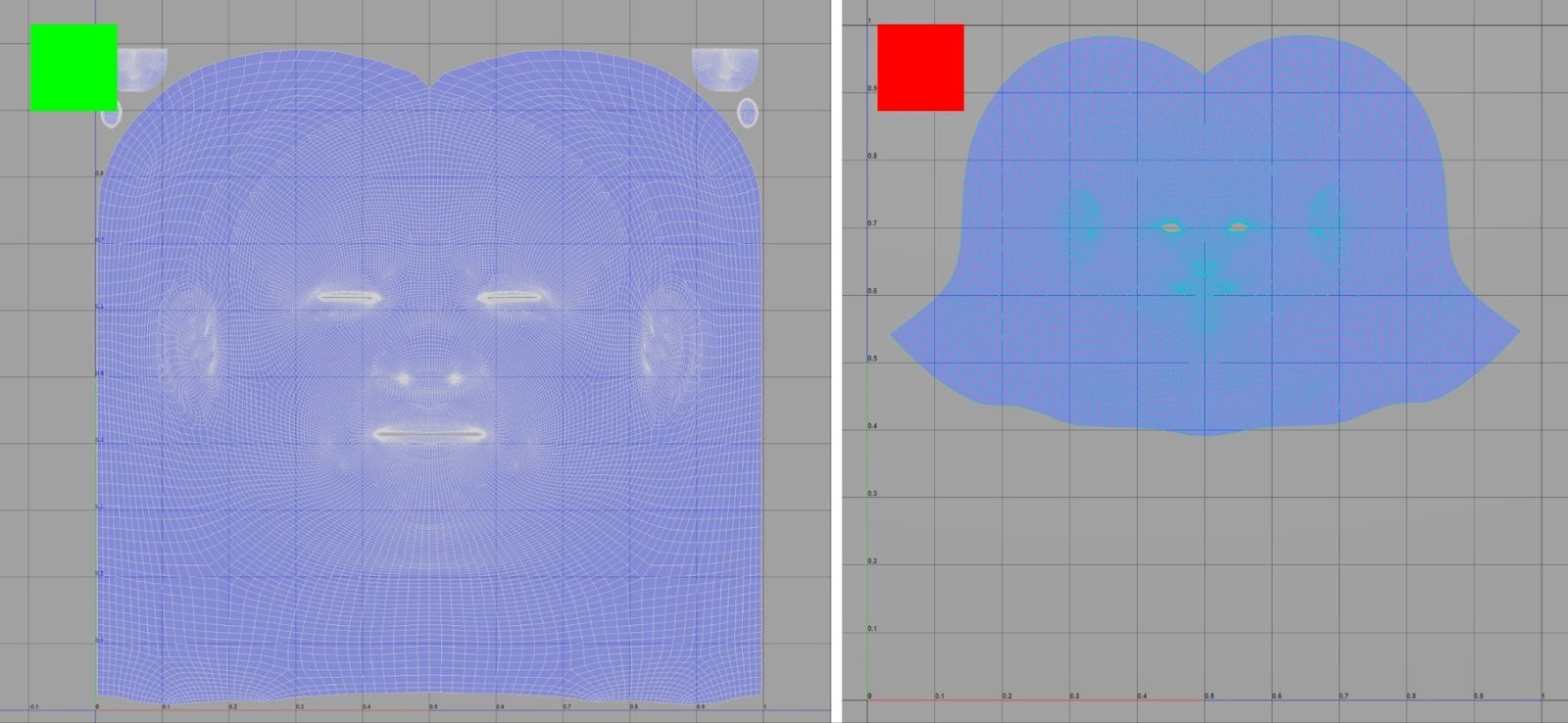
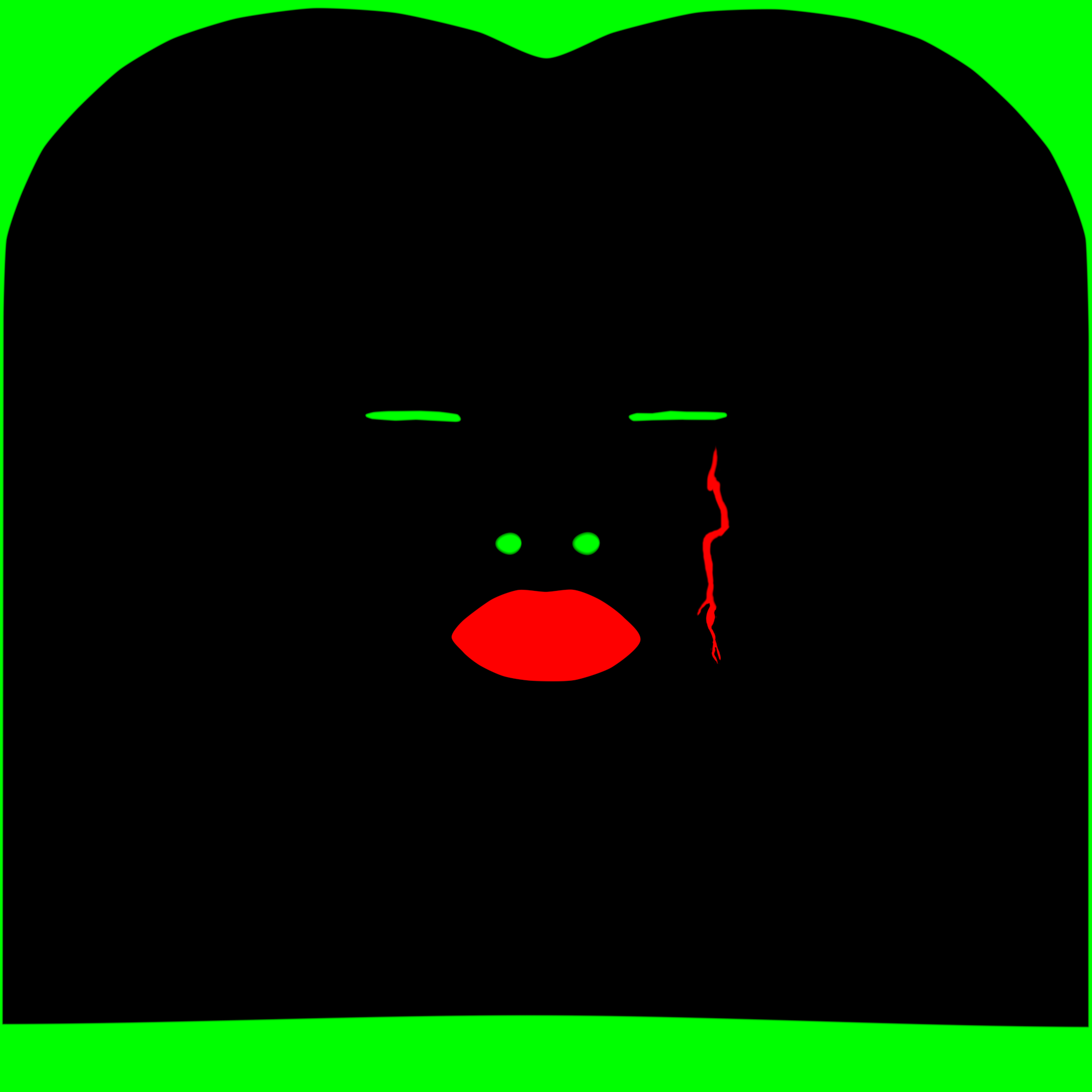
ID Mask
The ID mask allows SKAP to treat different regions of the asset appropriately and avoid unwanted artifacts.
While this ID mask is not mandatory, it is strongly recommended to exclude non-skin elements and improve the overall quality of the results.
The mask uses two channels:
- Red channel (R) - low-frequency features: SKAP processes skin and lips differently. Isolating the lips and other low-frequency features such as large scars in the red channel enables more precise and controlled treatment.
- Green channel (G) - non-skin masking: These areas are removed from processing and automatically filled, preventing unwanted artifacts. Useful for hair, accessories, and eye and mouth sockets.

GET STARTED
Get started with your own asset
Upload your OBJ and baseline maps and start your first SKAP project !
